

The rise of IoT
Managing customer quality of experience (QoE) in the IoT era
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is many things to many people. Everything from new applications, such as smart cities or autonomous vehicles to massive sensor networks for monitoring environmental or industrial systems.
It also means a fundamental change in the way mobile network operators build and manage networks to remain profitable.
The anticipated massive scale, combined with a lower average revenue per connected device, is bringing about the most significant change yet in network architectures.
Does your network have the visibility needed to manage this transformation? Will your existing mobile services be impacted by IoT-driven changes?
EXFO has the expertise and solutions you need to make sure your networks continue to perform flawlessly as you transition into the IoT era.

Challenges
How will IoT impact networks?
Every IoT service has different requirements for things like device density, data rates, latency and mobility to name just a few. And each network presents a unique set of operational challenges which need to be planned for now. IoT devices are expected to outnumber traditional mobile devices by 2018, dramatically changing services in the network.
Are you ready to manage these challenges?
Declining average revenue per user
Current mobile networks are built for today’s mobile broadband (MBB) users and priced accordingly. Wide scale IoT applications cannot afford MBB service pricing, so operators will need to charge significantly less for them if they are to attract IoT service providers. Combine this with the expectation of 30 to 50 billion IoT devices in service by 2020 and it becomes clear that how mobile networks are built must also change. This was the main driver behind the new reference architecture specified in the 3rd Generation Partnership Project's (3GPP's) release 13.
But how will these changes impact existing MBB services? Will the architectural enhancements for IoT negatively affect current services?
The key for managing this transformation will be visibility into how the mobile network, the existing mobile services and the new or enhanced service elements perform while the changes are being implemented.
New 3GPP architecture
In June of 2016, the 3GPP Forum published release 13 of the 3GPP reference architecture for mobile networks, specifically to address the requirements of IoT applications. This new architecture fundamentally changes the functionality of several elements of the architecture and introduces new ones. The intent was to address the impact that massive IoT deployments would have on mobile networks.
But how will these changes impact the quality of the traditional mobile broadband (MBB) services; which will continue to generate significant revenue? Will the changes be able to address the needs of IoT without impacting the quality of experience (QoE) for MBB users?
The key for managing this transformation will be visibility into how the mobile network, the existing mobile services and the new or enhanced service elements perform while the changes are being implemented.
Low power wide area coverage
IoT applications, such as remote sensors, smart meters or asset tracking, need to be able to operate over very long distances or difficult locations such as building interiors, subway tunnels or even buried underground. To address this, new wireless technologies, such as 3GPP narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M or LoRa and Zigbee, are being introduced; some are standards based while others proprietary, operating in either licensed or unlicensed spectrum.
But how can you be sure the application will work at scale? With expectations of 200,000 IoT sensors or more per square km, being able to test and monitor these devices—including the radio interfaces—to be sure they meet, and continue to meet the application needs will be critical to the overall success of the solution.
Tighter latency requirements
The Internet of Things is not just about sensors and smart meters. It also includes applications such as connected vehicles, smart traffic management, and remote video monitoring. These applications demand extremely low latency (< 1ms in some cases) to ensure the safety of passengers or to provide real-time high definition video for security surveillance.
Ensuring your network is up to the task of meeting these requirements means continuous, active monitoring of the end-to-end service in real-time. Advances in networking technology, such as virtualization and network slicing, will enable ultra-low latency applications, but will require performance monitoring to become an embedded function of the service itself, rather than a network feature.
Massive scalability demands automation
According to many analysts, there may be as many as 50 billion IoT devices globally by 2020. Even if this number is off by 25 billion, the number of IoT devices will dwarf the number of mobile broadband phones. This ramp up of IoT presents a huge challenge for installation, testing and provisioning activities as well as from the perspective of ongoing monitoring and maintenance.
Simply put, if automation is not at the center of operations, IoT will require an insurmountable effort. Test orchestration, real-time 3D analytics and integration of all operations processes into a closed loop optimization solution is a must.

Solutions
How IoT helps the telecommunications industry?
The rise of IoT will drive a fundamental discontinuity in the service provider market. And while change can have a negative impact, companies that embrace the inevitable, often emerge better than before. IoT can be the catalyst that drives carriers to modernize their service innovation model, streamline operations through automation and become an innovative leader in the transformed network.
Does your network provide the insight needed to successfully manage this change?
New revenue opportunities
As competition in the communications markets become more intense and customers, both business and individuals, demand ever more intelligent and valuable services to help simplify their daily routines, communications service providers (CSPs) of all types are looking for new ways to expand their markets and broaden their service portfolios. IoT does just that by providing a platform to launch innovative new services. Everything from smart factories (Industry 4.0) and smart wearables (clothes, fitness trackers) to smart transportation (connected vehicles, intelligent traffic lights) and smart meters (gas, electricity, water) fall within the scope of the CSP.
Carriers that embrace the IoT era will not only benefit from the additional revenue opportunities, but they will also gain a significant competitive advantage through leadership in this new communications reality.
IoT will be the enabler for sustainable competitive advantage and revenue growth.
Lead application for 5G
The wireless industry is intensely focused on the development of 5G technology and carriers are beginning to invest in upgrades to their existing network. However, for many of these carriers, the primary driver for 5G remains unclear. In fact, 5G really only brings two distinct advantages over existing LTE solutions–higher bandwidth and lower latency. Much has been written to suggest that existing mobile broadband services do not actually require 5G to remain competitive.
On the other hand, there are IoT services being developed and planned for that will require greater bandwidth and lower latency. IoT services such as video monitoring, connected vehicles, automated traffic control or remote medicine could not be possible without 5G technology.
IoT may very well be the ‘killer app’ that truly justifies the significant investments required to build a 5G network.
Data-driven service analytics
Perhaps one of the biggest benefits of operating an IoT network will be the insights gained into customer and network behavior. Because of the massive scale expected in IoT networks, fully automated network operations will be an absolute necessity; manual operations will simply not scale to the volume of deployments or be able to effectively keep the network operating efficiently.
Underlying this automation will be highly sophisticated analytics tools generating millions of KPIs daily to keep track of the health of the network and services. This data can then be analyzed to extract service and usage trends, identify key growth markets and new service opportunities. It can also be used to continually assess and improve the overall quality of the network to ensure competitive advantage is maintained.
So while IoT will certainly drive additional services and revenue, it’s biggest benefit may be in creating an analytics-based engine for growth.
Partner for service innovation
The IoT market is rapidly evolving as new service ideas and concepts seem to appear almost daily. These new applications and services require a highly reliable, broad-reaching network to connect the IoT devices back into the IoT service provider. Partnerships with leading edge IoT connectivity providers and emerging IoT service providers will open up additional growth opportunities and competitive advantage for both parties.
Connectivity providers with international reach will be especially attractive to IoT service providers since many business applications require a multi-national footprint.
Leveraging your existing network footprint to provide IoT connectivity services will be appreciated by your existing customers venturing into the world of IoT and will make your network more attractive to the leading IoT providers.
Simplified operations and maintenance
By virtue of its anticipated massive scale, IoT will demand a heavy reliance on automation for commissioning devices, provisioning services, optimizing networks and detecting and resolving network and service issue. And, since IoT is all about machine to machine communications, detecting and reporting issues is likely to be automated.
Continuous service assurance monitoring, multidimensional analytics, spanning customer, network and service, and real-time KPI reporting means many issues can be detected and resolved before they're noticed.
IoT promises to lower the average cost of operations per service, improving your bottom line while at the same time providing your customers with a better quality of service.
IoT use cases and solutions
There is no one-size-fits-all for IoT, but there is a common need—quality of service. Having clear visibility into network and service performance is critical to the success of every IoT application. Testing, monitoring and assuring must be integral to every solution. From industry leading handheld test sets to virtualized assurance solutions to real-time analytics platforms to simulators for network and equipment validation, EXFO has the solutions to support any IoT network.
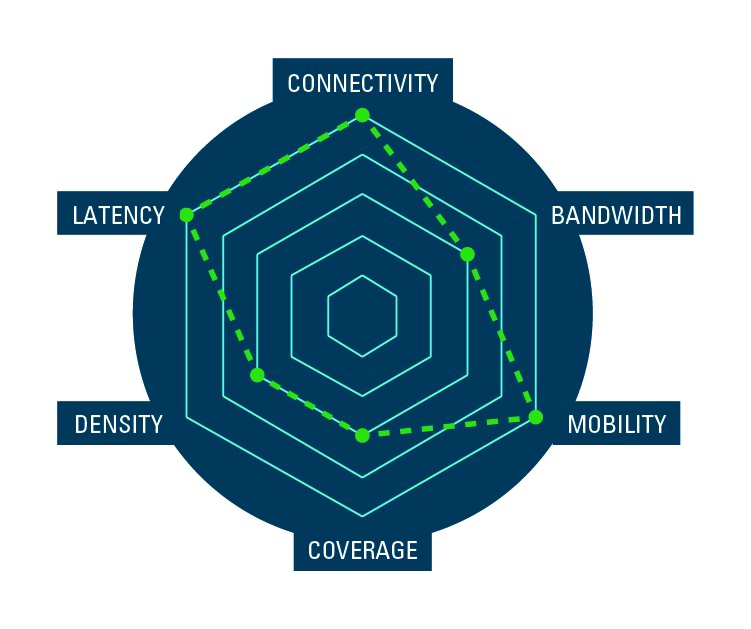
Connected vehicles
Roads filled with self-driving vehicles and skies filled with drones; an emerging reality that, without a centralized control system ensuring the safety of vehicles and people, would result in chaos.
For such a control system to work, the network needs to be fast (< 1 ms latency), always on (at least ‘six 9's’ availability) and able to handle 1000’s of vehicles, moving at highway speeds across multiple cell sites.
Having the tools and expertise to ensure visibility and control of IoT networks and services throughout the entire lifecycle is critical for success.
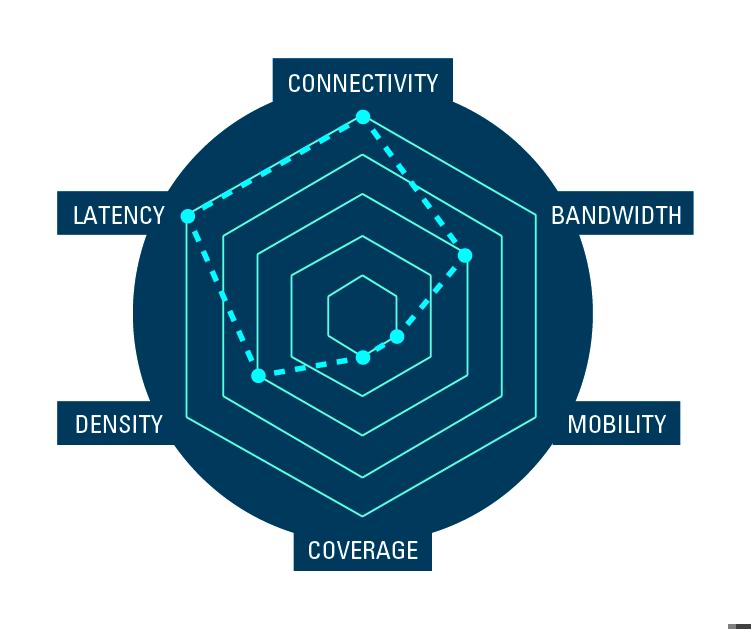
Industrial IoT
Hundreds of robots, all working with precision timing and coordination. Materials arriving exactly when needed and no time for unnecessary maintenance. This is the modern factory.
Having real-time visibility and control is essential to operations. The IoT network needs to support always-on, real-time communications to ensure things are running as planned, and when they don’t, that downtime and loss is minimized.
Having the right tools to visualize performance and availability are essential to achieving this goals.
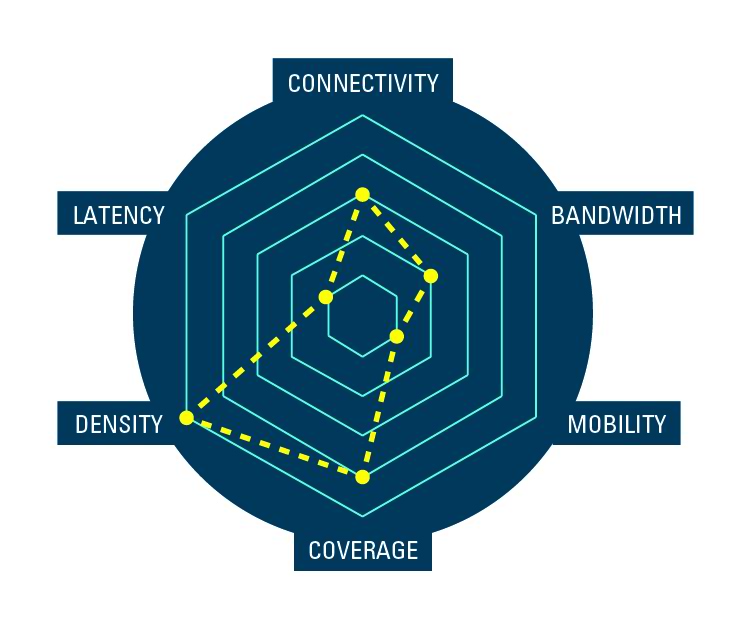
Smart meters
Hundreds of thousands of meters per square kilometer—possibly located in basements or interior rooms with limited access available—sleeping until it’s time to transmit a reading. That's the reality of smart meters.
Your challenges? Ensuring the meters are reachable by whatever air interface is being used. Having the network capacity to manage multiple thousands of meters ‘waking up’ and transmitting simultaneously. Accurate billing and minimized operations cost rely on flawless operation.
Having the right tools to stress test the network design and verify wireless connectivity is critical to achieving success.
Smart cities
Traffic lights that adapt to congestion or accidents. Sensors that report accidents or road conditions and automatically dispatch the appropriate help. Real-time connectivity to guidance systems that automatically provide the fastest route to your destination.
The network that supports this vision needs to be always on (six 9's availability) and able to cope with dense urban environments, without issue—especially during emergency events.
Having the right tools to stress test the network design and verify wireless connectivity is critical to achieving success.
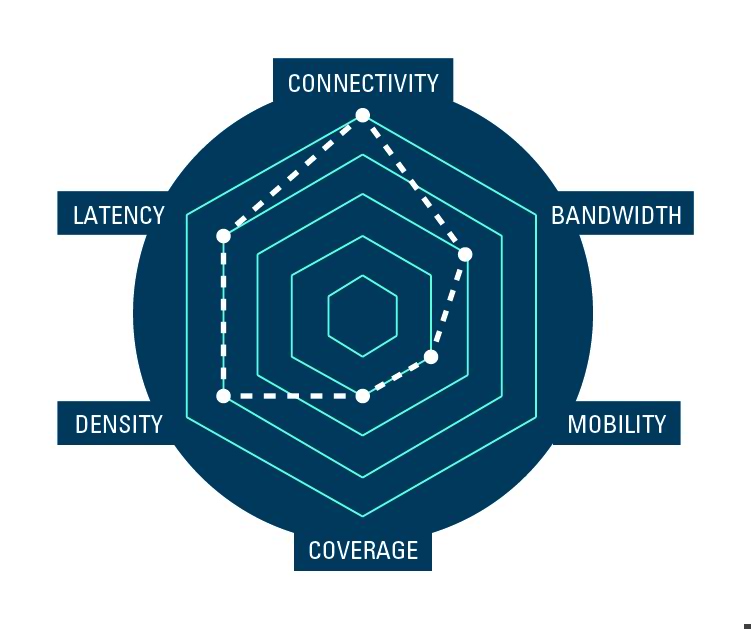
Smart agriculture
Remote sensors, distributed throughout the fields, orchards or vineyards for soil moisture and nutrient monitoring. Health and location sensors tagged to animals in the herd. Real-time maintenance status of farm equipment. This is the farm of today.
Farms covering thousands of acres, herds of thousands of cattle. Having the wireless coverage to connect when needed is critical to ensuring crop and livestock health.
Having the right tools to verify wireless connectivity and detect failures in a timely manner are critical to the success of modern farming operations.
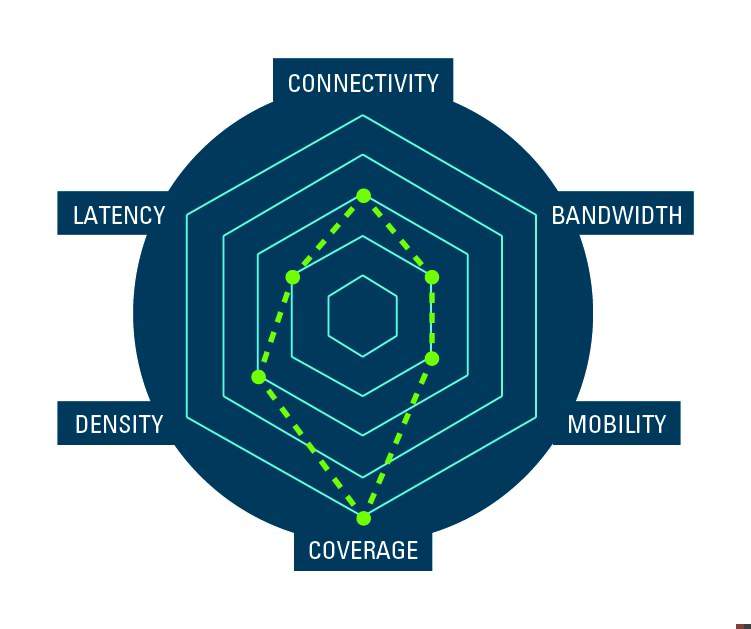
Asset tracking
Hundreds of thousands of cargo containers carrying thousands of pieces of goods, all part of hundreds of thousands of ‘just-in-time’ (JIT) supply chains. Keeping track of all this inventory, globally, is what drives efficiency in the modern factory.
A global network that supports a wide range of wireless access technologies, for high density, high mobility shipping and in near real-time to support JIT supply chains is critical to today’s cost-optimized factories.
Having the right tools to stress test the network design and verify wireless connectivity is critical to achieving success.
Resources
All resourcesLanguage
Resource type
